Abstract
Elevation of soluble Stimulation-2 (sST2) is considered a prognostic biomarker in several disease progression, such as cardiac allo-rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and is associated with the response to tissue damage that secrets Interleukin-33 (IL-33), an alarmin. sST2 is an alternatively spliced isoform of the Interleukin 1 Receptor-Like 1 (IL1RL1) gene that also encodes the major membrane-bound ST2 (ST2) isoform expressed on tolerogenic immune cells including Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs), type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), type 2 helper T cells (Th2), monocytes, M2 macrophages, mast cells, eosinophils and neutrophils. IL-33 is the only known ligand that binds to both sST2 and ST2. Binding of IL-33 to ST2 activates intracellular signaling in ST2 expressing cells whereas sST2 functions as a decoy receptor to sequester the secreted free IL-33. After allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), elevated sST2 levels are associated with patients with GVHD resistant to steroid therapy and with subsequent non-relapse related death. We hypothesized that therapeutic intervention to release IL-33 from sST2 may modulate the T cells responses for treating GVHD. As proof-of-concept, we have reported studies using either ST2 antibodies (Zhang et. al., Sci. Trans. Med. 2015) or small-molecule ST2 inhibitors (iST2-1 in Ramadan et. al., JCI Insight, 2018) in the murine GVHD models. Herein, we report a novel series of small-molecule ST2 inhibitors from our follow-up development of iST2-1. We show a representative compound, XY-52, effectively reduced sST2 levels, alleviated GVHD and improved survival in a murine GVHD model.
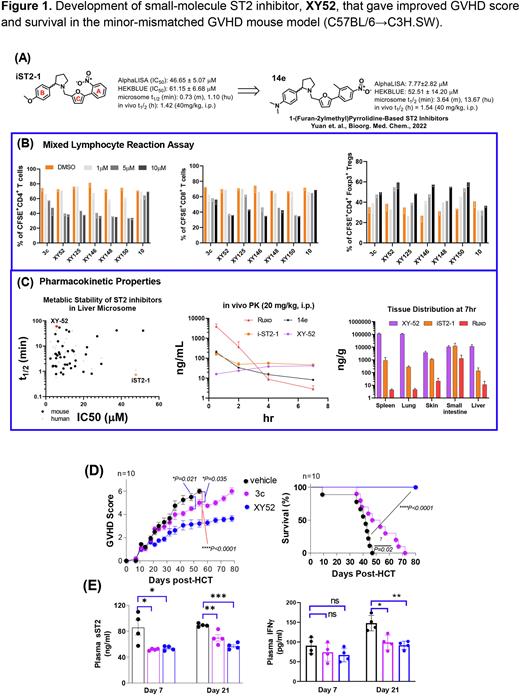
Based on our previously discovered iST2-1, we recently developed 1-(furan-2ylmethyl)pyrrolidine-based ST2 Inhibitors and constructed the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of compounds against ST2/IL-33 binding (Yuan et. al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2022). That study led to identify 14e (Fig. 1A) that has an IC50 value of 7.77 mM against ST2/IL33 binding determined by the AlphaLISA assay. Despite the improvement of the IC50 value as compared to iST2-1, 14e has deficiency in solubility and metabolic stability (including a similar in vivo half-life as iST2-1) that required further optimization. To improve 14e, we first focused on replacing the furan group (C-ring) of 14e with the goal of eliminating the potential metabolic issue of the furan group. We found replacement of furan by either a pyrrole (ST2-J-100) or an alkylated pyrrole group (ST2-J-106, 107) retained the activity of the inhibitors. We then investigated the replacement of the chemical groups on A and B rings of 14e aiming to improve the solubility of the inhibitors while maintaining their activities. These modifications led to identify a new series of ST2 inhibitors represented by XY-52. In the mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) assay, we found XY-52 and analogs (XY-125, XY-146, XY-148, XY-150) inhibited CD4+, CD8+ T cell proliferation while increased Tregs (Fig. 1B). XY-52 has improved in vitro (t1/2= >60m in mouse, 41m in human liver microsome) and in vivo metabolic stability. In vivo PK study showed that XY-52 has higher tissue distribution including spleen, lung, skin, small intestine and liver than iST2-1 or Ruxolitinib (Fig. 1C).
XY-52 was then selected to compare with 3c (previously reported) in a clinically relevant minor-mismatched GVHD mouse model (C57BL/6→C3H.SW). Using a 21-day prophylactic regimen of 40mg/kg/day (BID), we found that 3c reduced GVHD score (P=0.02) and extended survival (HR 3.90, P=0.02) in mice. Mice receiving XY-52 treatment had a more profound reduction in GVHD score (P<0.0001) and improvement in survival (HR, 31.22, P<0.0001) (Fig. 1D). Both 3c and XY-52 yielded lower plasma concentrations of sST2 and IFNg compared with the DMSO control (Fig. 1E) at Day 7 and 21 post-HCT. Ex vivo analysis of T cells in the gastrointestinal tract (GI) at day 21 post-HCT showed that XY-52 was more effective than 3c at reducing CD4+ IFNg+, CD8+ IFNγ+, CD4+ IL-17A+ T cells and increasing CD4+ Foxp3+ Tregs frequencies.
In summary, XY-52 represents a promising ST2 inhibitor that reduces the plasma sST2 levels, CD4+, CD8+ effector T cells and increases CD4+ Foxp3+ Tregs frequencies in in vitro and in vivo GVHD models. Further improvement in the potency and the PK profile of XY-52 will allow us to develop effective ST2 inhibitors for use as a prophylactic or therapeutic regimen for GVHD therapy.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal